Open Source Imaging Consortium (OSIC)
Powering Innovation in ILA & ILD Research with Global, AI-Ready Data
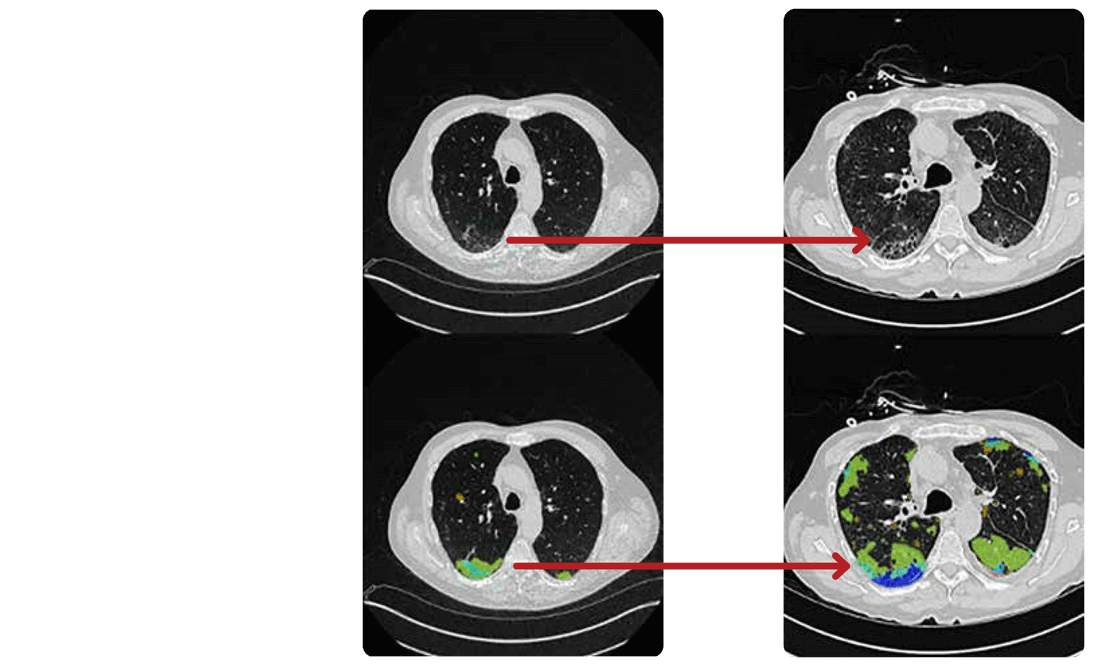
Explore the Subpleural Lung in 3D
Transforming Data into Interactive Insights with OSIC Cloud
About OSIC & the OSIC Cloud Data Repository
OSIC – a global 501(c)(3), not-for-profit cooperative effort between academia, industry and patient advocacy groups – was created to transform research in interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) and rare fibrosing lung conditions. At the heart of OSIC is the OSIC Cloud Data Repository (OSIC Cloud), the world’s largest and most globally-diverse ILD database. This curated and AI-ready repository houses a plethora of anonymized high-resolution CT scans, clinical data, and longitudinal follow-ups, and is fully GDPR and HIPAA compliant. We believe this first-of-its-kind database is the key to unlocking digital imaging biomarkers that can dramatically speed diagnosis and deepen understanding of individual prognosis and therapy response.
Watch our member video to learn more about our vision and mission.
How OSIC Accelerates Innovation
Powered by the collective expertise of radiologists, pulmonologists, machine learning pioneers, and imaging specialists, OSIC delivers a rich, diverse dataset that fuels transformative, AI-driven breakthroughs.
OSIC’s unique collaboration engine empowers every member to own their discoveries within a trusted ecosystem. As creators of the OSIC Cloud, we help accelerate scientific progress by providing access to multi-ethnic and multi-center datasets, platform usage for private and closed-loop trials, and a comprehensive knowledge hub with best-in-class educational and clinical research resources.
About The OSIC Cloud Platform
The OSIC Cloud, powered by vida, is a secure platform for managing de-identified, curated real-world and clinical trial data — designed to fuel collaborative lung disease research.
THE OSIC CLOUD FEATURES
Data Security & Privacy Compliance
- GDPR- and HIPAA-compliant architecture
- Robust data backup and security
- Automated cloud-based pseudonymization and anonymization
- Role-based access controls tailored to user types
- Built-in open and restricted access functionality
High-Quality, AI-Ready Data Infrastructure
- Highly curated datasets
- Rigorous QC through automated and manual reviews
- Automated data normalization
Adaptability & Scalability
- Configurable for diverse research workflows
- Disease-agnostic, multi-omic platform
- Support for 13+ languages
Powerful Collaboration & Research Tools
- Smart data upload and customizable contribution tools
- Integrated case viewer
- Annotation tools for collaborative research
- Advanced search and filtering
Expertise Driving Clinical Trial Excellence
- Clinical trial workflows and features optimized for imaging
- Worklist and collection management
- Site training and certification
- 24/5 trial site support for imaging-related questions
- Dedicated Clinical Engagement Team for global site QC and procedures
- Online access to reference materials, including protocols and radiology manuals
Clinical & Educational Impact
- Embedded e-learning platform
MULTI-OMIC DATA
Hear from ILD thought leaders who were part of our 2025 ATS Innovation Hub presentations.
From Incidental ILAs to Early ILD Detection
Leveraging OSIC’s Global Database
Recorded Monday, May 19, 2025
Learn how early-stage interstitial lung abnormalities (ILAs) detected in routine screenings can prevent progressive fibrotic lung disease. Discover the latest features of the OSIC Cloud platform, including advanced visualizations that highlight subtle lung changes, and hear vital insights from the Czech Republic’s national lung cancer screening program.
SPEAKERS
From Incidental ILAs to Early ILD Detection
Finding Hidden Clues within OSIC’s Global Database
Recorded Tuesday, May 20, 2025
Discover how we can detect fibrotic lung disease before it becomes visible. Learn how AI and advanced imaging technologies are transforming pulmonary medicine. Explore the features of OSIC’s global data platform, which now houses over 7,000 fibrosis lung disease scans, and find out how these advancements facilitate earlier interventions for high-risk patients.
SPEAKERS

Training AI to Detect ILA
OSIC is enabling researchers to train deep learning models to do just that.
- Early ILA detection using LDCT and HDCT
- Stratification of “at-risk” populations
- Potential for earlier treatment and better outcomes
AI + OSIC = New frontiers in preventive pulmonology
Can AI learn a risk score?*
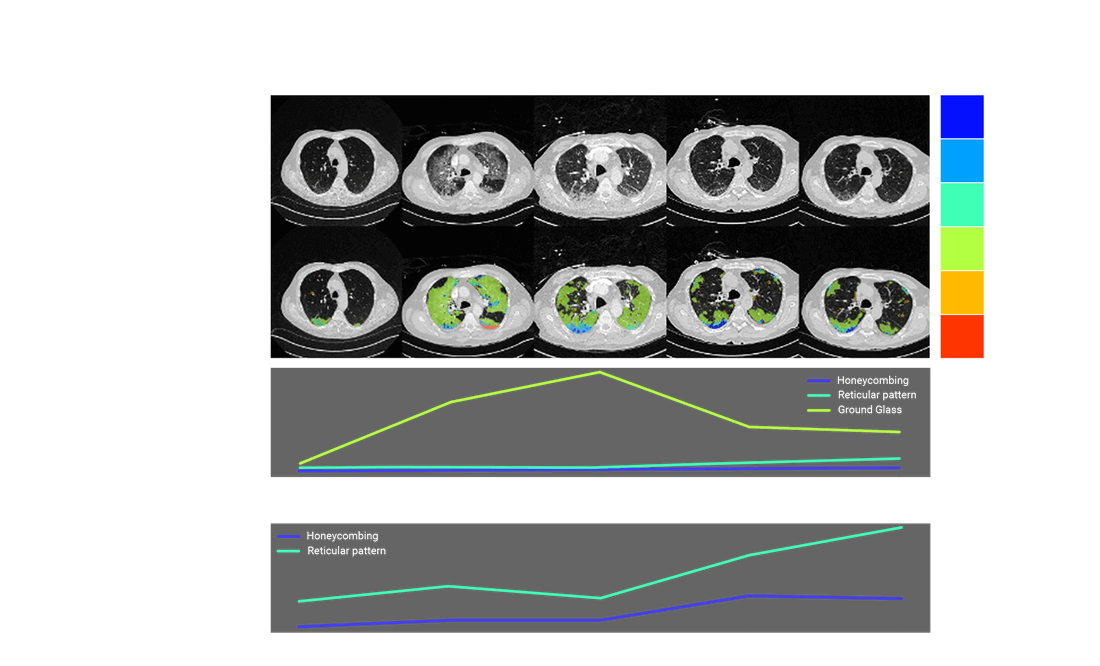
Unlocking Early Detection with AI ILA Risk Scoring
Enabling precision-driven, personalized management; minimizing missed and delayed diagnoses; enhancing outcomes through timely intervention.
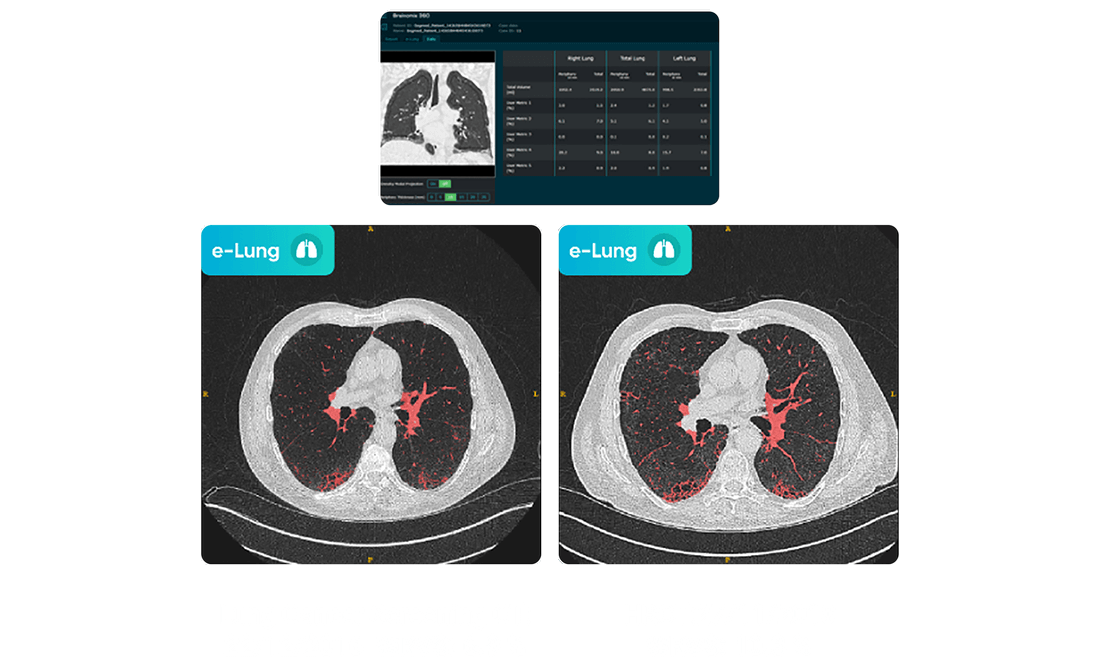
Discover Innovative Research Utilizing the Global AI-Ready OSIC Dataset
Explore groundbreaking studies using OSIC. Researchers worldwide are leveraging this rich resource to advance understanding and treatment of ILDs. With over 75 peer-reviewed publications and numerous conference presentations citing OSIC data, the data plays a pivotal role in driving innovation in fibrosing and rare lung diseases.
CenTime
Event-conditional modeling of censoring in survival analysis
OSIC provided a grant to University of London (UCL) to create algorithms to help advance digital imaging biomarkers for accurate imaging-based diagnosis, prognosis and prediction of response to therapy. Through this initiative, the UCL team created “CenTime: Event-conditional modeling of censoring in survival analysis.” This work aims to address key limitations in current survival analysis methods.
The algorithm has been trained and evaluated using the combination of real-world, high-resolution lung CT scans (HRCT), associated clinical data, and mortality labels from the OSIC Data Repository. CenTime has shown promising results in more accurately predicting survival probabilities. This has the potential to advance digital imaging biomarkers, not only for lung disease but for other diseases by addressing key limitations in current survival analysis methods and allowing for more accurate and reliable models.
Current Limitations
- The standard Cox model focuses only on ranking patients by survivability without estimating the actual event time.
- Other models in the literature treat the problem as a classification task, ignoring the time-ordered nature of events.
- Effective use of censored samples is often overlooked.
CenTime
- Directly estimates the event time.
- Features a novel machine learning method for leveraging censored training samples (samples where the exact death time is unknown).
- Encodes the ordinal nature of event time.
- Performs robustly even when uncensored data is scarce.
- Can be easily integrated into deep learning setups.
UCL compared CenTime with standard methods like the Cox proportional-hazard model and DeepHit. Results have indicated that CenTime offers state-of-the-art performance in predicting time-of-death while maintaining comparable ranking performance.

During this collaborative forum, attendees:
- Heard OSIC members present AI advances and innovations using OSIC data.
- Explored new OSIC Cloud features: easier data contribution, advanced filters, and collaboration tools.
- Discussed clinical data curation and its impact on drug development for fibrosing lung diseases.
- Reviewed inclusion of new cohorts like lung cancer screening, sarcoidosis, and alpha-1 cases.
- Introduced Project OPUS, applying AI to spirometry, environmental, and imaging data.
- Joined panel discussion on OSIC’s progress, early ILD research, and clinical data insights.
Explore what was presented and discussed during the OSIC AI/Biomarker Innovation Showcase:
Join Us in Amsterdam for the
2025 OSIC Annual Member Meeting
& AI/Biomarker Innovation Showcase
OSIC members are invited to gather in Amsterdam for our 2025 Annual Meeting. Connect with fellow members, explore groundbreaking advances in AI and biomarker innovation, and be part of the conversations shaping the future of our field.
Enabling Breakthroughs
Explore the Powerful Datasets Available Through OSIC
IMAGING MODALITIES
Standardized DICOM formats: HRCT, LDCT, X-ray, and Photon Counting CT (PCCT)
CLINICAL DATA
Curated and normalized from global contributors
PATIENT DIVERSITY
Ethics-cleared, internationally diverse population
ILD TYPES INCLUDED
IPF, Sarcoidosis, RA-ILD, Lung Cancer Screens, and more
AI COLLABORATION
Led by Prof. David Barber, OSIC’s ML lead and Director, UCL Centre for Artificial Intelligence
The OSIC Cloud ILD Database: Data Overview
The OSIC Cloud Lung Cancer Screening/ILA Database: Pilot Overview
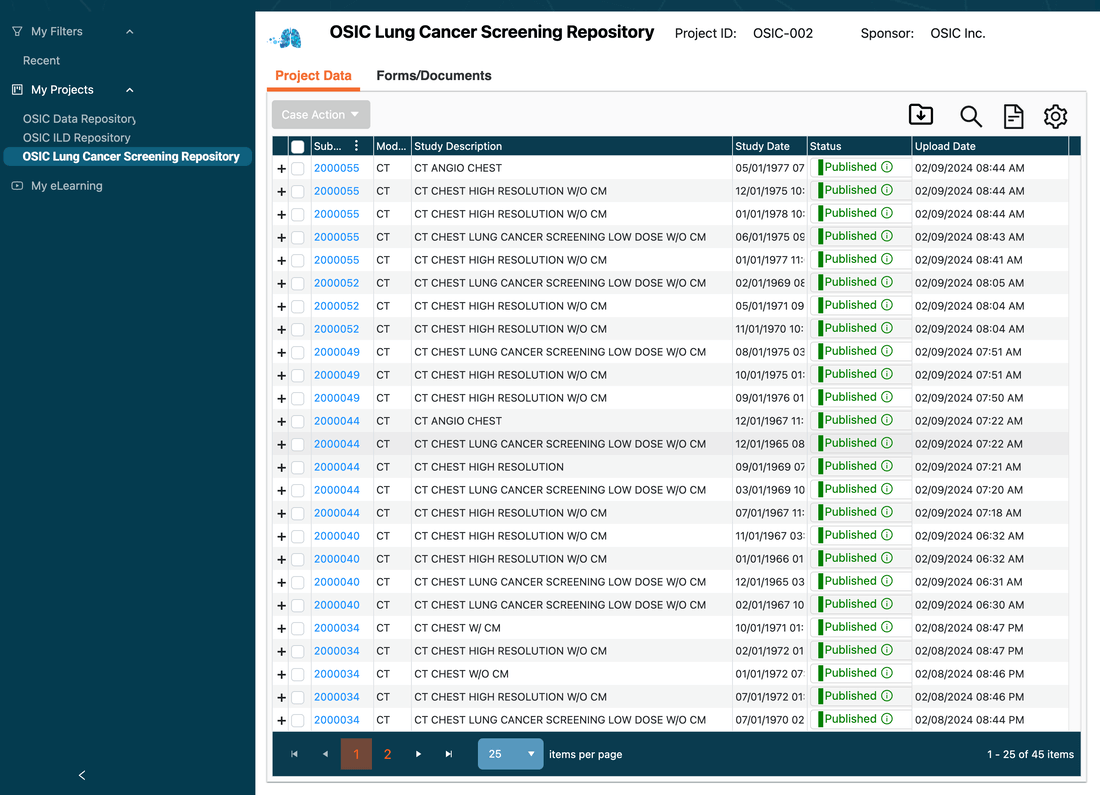
In a recent study of 1,384 individuals who received a lung cancer screening via CT scan, researchers identified “4% ILA in a lung cancer screening cohort; 37% had radiologic progression of ILA at 1 year and 40% were diagnosed with ILD within 5 years. Fibrotic ILA, defined by the presence of traction bronchiectasis, was a strong predictor of mortality, reduced progression-free survival, and diagnosis of ILD.”
The lung cancer cohort in our database will allow for future research to help identify biomarkers that can predict ILA/ILD disease progression.
The presence of ILA on a lung cancer screening is a significant finding that can increase the risk of developing ILD and may be associated with a higher risk of mortality. Early detection and appropriate management of ILA may crucial in preventing the progression to ILD and improving long-term outcomes.
Join Us: Collaborate and Innovate with OSIC
At OSIC, we’re always eager to collaborate and form partnerships that push the boundaries of rare lung disease research. If you have an innovative idea or simply want to explore opportunities with us, we’re open and ready to connect. Let’s work together to advance science and improve patient outcomes.
Institutional Partners
These organizations have made multi-year commitments of funding and/or pledged to contribute with imaging and clinical data or with other means to OSIC to ensure that it is positioned for success.
Learn more about OSIC
We encourage you to contact us to discuss our mission, the OSIC Cloud Data Repository, and how you can help make a difference in the fight against IPF and ILDs. Additional partners, collaborators and contributors are welcome and encouraged.